Song Structure
Most popular songs follow a common structure to ensure they are engaging and memorable. Here are some of the most used song structures:
1. Verse-Chorus Form
- Verse: Tells the story of the song, with lyrics that change in each verse but a consistent melody.
- Chorus: The main message of the song, often repeated with the same lyrics and melody. It’s usually the most memorable part.
- Example Structure: Verse 1 – Chorus – Verse 2 – Chorus – Bridge – Chorus
2. AABA Form
- A Section: The main melody and theme of the song.
- B Section: Provides contrast to the A section, often called the bridge.
- Example Structure: A – A – B – A
3. Verse-Pre-Chorus-Chorus Form
- Pre-Chorus: A section that builds tension and leads into the chorus.
- Example Structure: Verse 1 – Pre-Chorus – Chorus – Verse 2 – Pre-Chorus – Chorus – Bridge – Chorus
4. Bridge
- Bridge: A contrasting section that breaks up the repetition of the verse and chorus. It provides variety and usually occurs only once.
- Example Structure: Verse 1 – Chorus – Verse 2 – Chorus – Bridge – Chorus
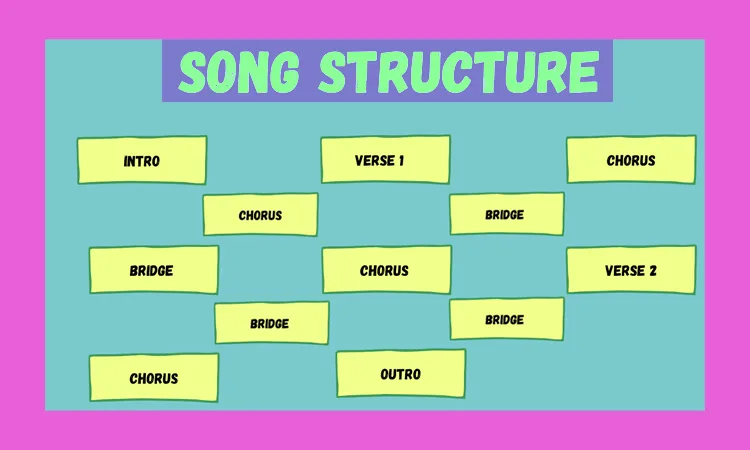
Example of a Common Pop Song Structure
- Intro: Sets the tone and introduces the song.
- Verse 1: Introduces the theme and story.
- Chorus: Highlights the main message and hook.
- Verse 2: Continues the story with additional details.
- Chorus: Repeats the main message.
- Bridge: Provides a contrast and new perspective.
- Chorus: Repeats the main message for a strong finish.
- Outro: Concludes the song, often with a fade-out.
Understanding and utilizing these basic concepts and structures will help you create cohesive and engaging music that resonates with listeners.